Karine SERRE, PhD
IMMUNOLOGIST
Latest Posts
21/01/2016
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease and NOT a chronic inflammatory disease!12/05/2015
CALL For PAPERS: “Innate T Cell Development and Functions in Immune Diseases”28/08/2014
XL Annual Meeting of the Sociedade Portuguesa de Imunologia 13-15th October 201413/04/2013
Beginnings of breaking down the differentiation program of innate IL-17-production27/01/2013
The improbable trio NKG2D – γδ T cells – IgE!!Helios
Is Helios a novel transcription regulator of Th2 commitment in vivo?
Our studies have uncovered a previously unrecognized transcription factor –Helios that belongs to the Ikaros family- that may play a key role in the regulation of Th2 cytokine production in vivo. Helios is a zinc-finger DNA-binding protein that belongs to the Ikaros family that has 3 other members: Aiolos, Eos, and Pegasus. Ikaros, the founding member of the family, is expressed in most hematopoietic cells, whereas Helios is expressed primarily in T-lineage cells and early multipotential precursors (1, 2).
We show here that Helios expression is strongly associated with the differentiation of naïve CD4 T cells into IL-4-producing Th2 cells in vivo.
Helios is specifically induced when CD4 T cells develop in vivo to Th2 cells
To get insight into the mechanisms that trigger IL-4 secretion by CD4 T cells in vivo we have studied in detail the response to a well characterized Th2-antigen – alum-precipitated ovalbumin (OVA). This research has compared the differentiation of OVA-specific transgenic CD4 (OTII) T cells primed in vivo to different forms of OVA. Alum-precipitated OVA (alumOVA) induces a Th2 immune response, associated with GATA-3 up-regulation and IL-4 secretion by a proportion of the responding OTII cells (3,4). It also promotes the class switching by B cells to IgG1 and IgE (5-8). By contrast, live attenuated Salmonella typhimurium engineered to express an ova transgene (provided by Dr. Cunningham, University of Birmingham, UK) induces OVA-specific Th1 responses, in which T-bet – the Th1 master transcription factor – is up-regulated and IFN-g produced by OTII cells (4, 9).
 Profiling of OTII cells was used to assess differential gene expression induced by these two forms of OVA in OTII cells from lymph nodes isolated 3 days after immunization. The transcription factor Helios was only expressed in CD4 T cells responding to the Th2-antigen – alum-precipitated OVA (4) (Fig. 1). In addition, work with Dr. Cunningham has shown that Helios is also selectively up-regulated during response to flagellin; another Th2-antigen. Helios is not induced in CD4 T cells responding to the Th1-antigen, highlighting the selectivity of its up-regulation in Th2-responses.
Profiling of OTII cells was used to assess differential gene expression induced by these two forms of OVA in OTII cells from lymph nodes isolated 3 days after immunization. The transcription factor Helios was only expressed in CD4 T cells responding to the Th2-antigen – alum-precipitated OVA (4) (Fig. 1). In addition, work with Dr. Cunningham has shown that Helios is also selectively up-regulated during response to flagellin; another Th2-antigen. Helios is not induced in CD4 T cells responding to the Th1-antigen, highlighting the selectivity of its up-regulation in Th2-responses.
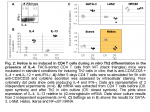
Helios is not induced when CD4 T cells are directed by IL-4 in vitro to produce Th2 cytokines
On of the reason for Helios not attracting attention previously maybe due in large part because of an over-reliance on an in vitro model of Th2 cytokine induction. Consistent with our data and hypothesis, that Helios is important in vivo but not during in vitro polarization, Helios is not induced in CD4 T cells cultured in Th2-skewing conditions (Fig. 2). Finally, a recent report has shown that like NF-kB1, Helios is dispensable for the Th2 polarization of naive CD4 T cells in the presence of IL-4 in vitro (10).
Conclusion
These results exemplify the major differences in the regulation of Th2 cytokine production in the in vitro and in vivo systems and highlights the importance of studying Th2 cell development in vivo. Thus it is possible that Helios has a novel role as a transcription factor that regulates the differentiation of naïve CD4 T cells into Th2 cells and I am currently investigating this hypothesis.
References:
1. Kelley, C. M., T. Ikeda, J. Koipally, N. Avitahl, L. Wu, K. Georgopoulos, and B. A. Morgan. 1998. Helios, a novel dimerization partner of Ikaros expressed in the earliest hematopoietic progenitors. Curr Biol 8:508-515.
2. Hahm, K., B. S. Cobb, A. S. McCarty, K. E. Brown, C. A. Klug, R. Lee, K. Akashi, I. L. Weissman, A. G. Fisher, and S. T. Smale. 1998. Helios, a T cell-restricted Ikaros family member that quantitatively associates with Ikaros at centromeric heterochromatin. Genes Dev 12:782-796.
3. Serre, K., E. Mohr, K. M. Toellner, A. F. Cunningham, R. Bird, M. Khan, and I. C. Maclennan. 2009. Early simultaneous production of intranodal CD4 Th2 effectors and recirculating rapidly responding central-memory-like CD4 T cells. Eur J Immunol 39:1573–1586.
4. Serre, K., E. Mohr, K. M. Toellner, A. F. Cunningham, S. Granjeaud, R. Bird, and I. C. MacLennan. 2008. Molecular differences between the divergent responses of ovalbumin-specific CD4 T cells to alum-precipitated ovalbumin compared to ovalbumin expressed by Salmonella. Mol Immunol 45:3558-3566.
5. Mohr, E., K. Serre, R. A. Manz, A. F. Cunningham, M. Khan, D. L. Hardie, R. Bird, and I. C. MacLennan. 2009. Dendritic cells and monocyte/macrophages that create the IL-6/APRIL-rich lymph node microenvironments where plasmablasts mature. J Immunol 182:2113-2123.
6. Cunningham, A. F., K. Serre, K. M. Toellner, M. Khan, J. Alexander, F. Brombacher, and I. C. MacLennan. 2004. Pinpointing IL-4-independent and IL-4-influenced acquisition and maintenance of Th2 activity by CD4 T cells. Eur J Immunol 34:686-694.
7. Cunningham, A. F., K. Serre, E. Mohr, M. Khan, and K. M. Toellner. 2004. Loss of CD154 impairs the Th2 extrafollicular plasma cell response but not early T cell proliferation and interleukin-4 induction. Immunology 113:187-193.
8. Cunningham, A. F., P. G. Fallon, M. Khan, S. Vacheron, H. Acha-Orbea, I. C. MacLennan, A. N. McKenzie, and K. M. Toellner. 2002. Th2 activities induced during virgin T cell priming in the absence of IL-4, IL-13, and B cells. J Immunol 169:2900-2906.
9. Cunningham, A. F., M. Khan, J. Ball, K. M. Toellner, K. Serre, E. Mohr, and I. C. Maclennan. 2004. Responses to the soluble flagellar protein FliC are Th2, while those to FliC on Salmonella are Th1. Eur J Immunol 34:2986-2995.
10. Cai, Q., A. Dierich, M. Oulad-Abdelghani, S. Chan, and P. Kastner. 2009. Helios Deficiency Has Minimal Impact on T Cell Development and Function. J Immunol 183:2303-2311.